Before I go into detail, let me tell you in brief that V-Sync, G-Sync, and FreeSync are technologies used in laptops and personal computers to deliver an improved gaming performance in terms of visual stability on the monitor. In other words, these three terms are related to graphics displayed on the monitor of the PC or laptop.
Such technical terms often confuse people and that’s why I’m about to discuss all of them here. Among that three technologies (V-Sync, G-Sync, and FreeSync), V-Sync was the first one to be used by laptop manufacturers to offer a stable graphics performance.
If you gain valuable solutions then follow Laptop Radar for more future learning.
V-Sync
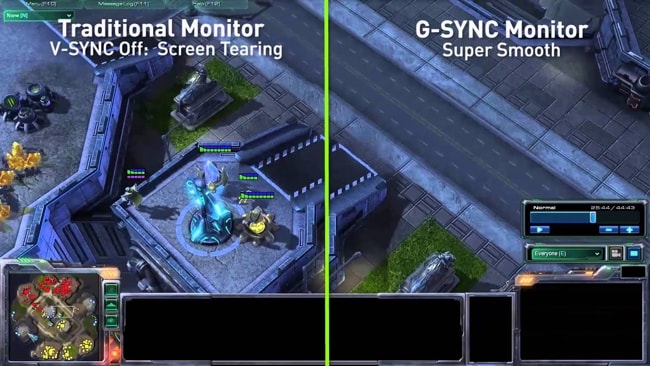
The full form of V-Sync is Vertical Synchronization. Its purpose was only to prevent screen tearing and stuttering.
A screen tearing is something like a horizontal kind of line that shows up when two frames interact on the computer display at the same time.
In simple words, it’s nothing but the distortion you see in the image. Screen sluttering is also a colleague of tearing.
Screen sluttering occurs when the refresh rate of the screen mismatches with the rate at which the GPU sends the data to the screen.
So, when the screen refresh rate becomes less compared to the rate at which GPU sends the data, screen tearing occurs. And, vice versa let the machine pause. Both cases result in a poor gaming experience. Both are disasters in the gaming world.
To eliminate that, V-Sync technology came into existence. It basically puts a cap on the GPU’s FPS (Frame Per Second – it’s the number of frames the GPU sends per second) to match the refresh rate of the screen.
Hence, If you use a monitor with a 60Hz refresh rate for gaming and GPU FPS is 80Hz or more, then V-sync will cap its speed by lowering the performance to match the legacy standards. It basically prevents the GPU from achieving the peak-performance.
But, it has certain limitations too. Back in the day, there were only 60Hz monitors. So, the V-Sync is only applicable to a 60Hz refresh rate monitor.
As V-Sync downgrades the High-end GPU’s performance, G-Sync came into existence. It has improved the performance quite a lot.
G-Sync
NVIDIA was the first company which has released the G-Sync technology in 2013. The main job of G-Sync is to ensure that there’s a smooth synchronization between the display’s refresh rate and GPU’s output rate.
G-Sync technology comes with a higher refresh rate display. In this case, the monitor’s refresh rate is always gonna higher than GPU FPS. So, this technology controls the screen refresh rate for smooth performance delivery.
Understand it by an example. Suppose the screen refresh rate is 240Hz and GPU FPS is 200Hz then it will create lag. In this case, G-Sync will interact with the screen and reduce the screen FPS by 40Hz to meet the equal value. This way, it enables smooth synchronization.
As a result, you will observe the smooth movement of graphics on the screen.
How G-Sync Work?
It will be very deep technical if I explain everything. Let me explain the basics.
To make FPS of GPU and screen, G-Sync manipulates the VBI (Vertical Blinking Interval). VBI interval is the time gap when the display finishes the drawing of the current frame and moves to the next one.
So, G-Sync featured monitor identifies this gap and modifies the refresh rate as per the GPU’s demand which in turn prevents frame drop issues.
Because G-Sync-enabled monitors are too expensive, every customer can’t get its benefits. In addition to that, NVIDIA has also released the most advanced version of G-Sync called G-Sync Ultimate. And, G-Sync only works with NVIDIA Graphics cards. As a result, AMD has introduced FreeSync.
FreeSync
FreeSync was released in 2015 by AMD. It’s a similar technology to G-Sync in terms of working. It’s developed to minimize screen tearing and sluttering noticeably. It’s specific to AMD GPU only. In addition, The “Free” in the name FreeSync tells that it’s free for manufacturers to implement.
A minor limitation of FreeSync is that it works on specific input tags. This means, it only works with DisplayPort 1.2a standard. It won’t work with a common legacy VGA or DVI port. So, FreeSync featured monitors are much cheaper compared to G-Sync.
But, FreeSync has one little drawback. You will find the ghosting effect of the image.
A Ghosting-like image occurs when the object moves to the next position but leaves the bit behind that feels like the part that’s behind the current position is a shadow or some sort of ghost-like.
But, In my experience, it’s in very rare case. But, it does exist. The primary cause of ghosting in FreeSync monitors is the improper power input. The low or overpowering input creates a gap between movements.
To overcome this limitation of FreeSync technology, AMD has introduced the next advanced version of FreeSync called FreeSync 2 HDR. With FreeSync 2 HDR, if the frame rate falls below the supported range of the monitor, low framerate compensation (LFC) is automatically enabled to prevent stuttering and tearing.
All monitors don’t support FreeSync 2 HDR. Its requirements are
- HDR support
- Low Frame Rate Compensation capabilities
- An ability to switch between Standard Definition Range (SDR) and High Dynamic Range (HDR)
Read other related articles:
- What are the IPS, TN, and VA panels
- What is Display Rates? Difference: 60Hz, 120Hz, 144Hz, and 240Hz
- Screen colour gamut SRGB, AdobeRGB, NTSC, and DCI-P3
- What are Display Nits
- Screen contrast ratio: What does it mean
- What’s is precision-enabled touchpad
- What is Cinebench Score
- CPU Undervolting explained
- What is AIDA64 and Why we use it for CPU and GPU stress tests?
- What is Windows Hello unlock?
- Difference between V-Sync, G-Sync, and FreeSync
If you gain a valuable solution from us then follow us and share this useful information with friends.
Laptop Radar is the only one who really tested the laptop first and then write laptop reviews so it definitely help you in the future also so join us now on all platforms to stay updated with the latest technology.
Remarkable! Its genuinely remarkable piece of writing, I have
got much clear idea concerning from this article.